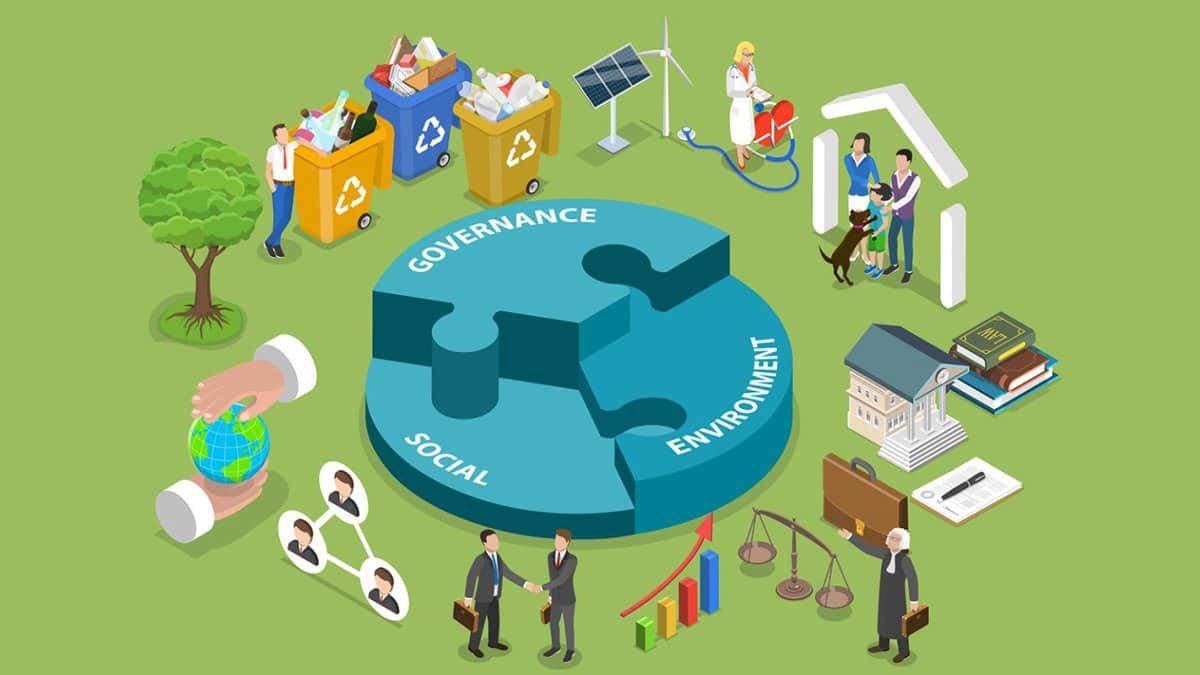
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting is an essential tool for companies to communicate their sustainability performance and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices.
ESG reporting enables companies to measure, track, and report on their progress toward sustainability goals and provides investors and stakeholders with the information they need to make informed decisions.

Investors are increasingly considering sustainability factors while making decisions, and ESG ratings are a significant factor that affects them. In the wake of growing pressure from stakeholders, including customers, employees, and regulators, it is important for companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
In this article, we will let you in on the alphabet soup of ESG and what it is supposed to depict. Since ESG reporting has become a key factor of corporate climate action, knowing how companies publish their reports and ascertaining their authenticity will be useful to assess the sincerity of following through with sustainability.
Decoding the Elements of ESG Reporting
ESG reporting has three important elements that encapsulate the essence of what it is. The alphabet soup can get complicated, but we will make it digestible for you. Have a look at what each of these elements is supposed to mean-
- Environmental factors may include issues such as carbon emissions, energy consumption, water footprint and waste management practices adopted by the company.
- Social factors encompass issues such as employee diversity and inclusion, labor practices, and community engagement initiatives the organization is a part of.
- Governance factors may include issues such as board composition, executive compensation, and anti-corruption policies.
What are the Compulsory Elements of an Ideal ESG Report?
An ideal ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) report should contain comprehensive and transparent information about the company’s performance on key issues. The report should cover the following areas:
- Environmental Performance: This aspect of ESG disclosure discusses the company’s environmental impact and sustainability initiatives. It consists of information about the company’s carbon footprint, energy consumption, waste management, and water usage.
- Social Performance: It covers the company’s social impact and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. This may include information about the company’s labor practices, human rights policies, community engagement, and diversity and inclusion efforts.
- Governance Performance: This section includes information about the board of directors, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and ethical business practices.
- Metrics and Data: An ESG report should include relevant data and metrics to provide readers with a clear understanding of the company’s ESG performance. The published document contains quantitative data, such as carbon emissions and water usage, as well as qualitative data, like case studies and examples of best practices.
- Goals and Targets: The report should also include information about the company’s ESG goals and targets. This will help stakeholders understand the company’s commitment to improving its ESG performance over time.
- Stakeholder Engagement: The report should describe the company’s approach to engaging with its stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, investors, and the communities where it operates.
- External Verification: Finally, an ideal ESG report should be externally verified by an independent third party to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data and information provided. This will help build trust with stakeholders and demonstrate the company’s commitment to transparency and accountability.
How do Companies Compile an ESG Report?
Here are some general steps a company can follow to compile an ESG report:
- Identify the material issues: The first step is to identify the ESG issues that are material to the company. Materiality refers to the issues that are most significant to the company and its stakeholders. The company can conduct a materiality assessment to identify these issues.
- Set targets and goals: Once the material issues have been identified, the company can set targets and goals for each issue. These goals should be measurable and time-bound.
- Collect data: The company needs to collect data on the ESG issues it has identified. This data can come from a variety of sources, including internal company systems, third-party audits, and industry benchmarks.
- Analyze data: Once the data has been collected, the company needs to analyze it to determine its ESG performance. This analysis can help identify areas where the company is doing well and areas where it needs to improve.
- Draft the report: The company can then draft the ESG report, which should include information on its ESG performance, goals, and targets. The report should also include a description of the company’s sustainability strategy and how it is integrating ESG considerations into its operations.
- Verify and validate the report: The company can have the report verified and validated by an independent third party. This verification can increase the credibility of the report and ensure that it is accurate.
- Publish the report: Finally, the company can publish the ESG report, making it available to stakeholders, investors, and the public.
It’s important to note that the specific process for compiling a report may vary depending on the company and the reporting framework they use.
Some companies may choose to use established frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), or the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) to guide them on how to draft an ESG report.
Frameworks That Utilise ESG Reporting
There are several frameworks that companies can use for ESG reporting, including the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Each of these frameworks has its own set of guidelines and reporting requirements, and companies can choose the framework that best fits their needs and goals.
GRI
The GRI framework is one of the most widely used frameworks for ESG reporting. The GRI guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for reporting on sustainability issues, including environmental, social, and governance factors.
The framework includes a set of standardized indicators that companies can use to report on their sustainability performance, as well as guidance on how to report on each indicator. The GRI also provides guidance on how to report on specific sustainability issues, such as climate change, human rights, and water.
SASB
The SASB framework is focused on materiality, meaning that it identifies the ESG issues that are most relevant to a company’s business and operations. The framework provides a set of industry-specific standards for reporting on ESG issues, and it is designed to be compatible with existing financial reporting requirements.
The SASB standards are organized around five categories: governance, environment, social capital, human capital, and business model and innovation.
TCFD
The TCFD framework is focused on climate-related financial disclosures. The framework provides a set of recommendations for reporting on climate-related risks and opportunities, and it is designed to help companies understand the potential financial implications of climate change.
The TCFD recommendations cover four areas: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
What are the Benefits of ESG Reporting?
ESG reporting is becoming increasingly important for companies as they seek to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and meet the expectations of investors and stakeholders.
However, it can be complex and time-consuming, and companies may need to invest significant resources to develop and implement a robust ESG reporting program. Despite these challenges, ESG reporting can provide significant benefits for companies, including improved stakeholder engagement, enhanced reputation, and better access to capital.
There are several benefits of ESG reporting, including:
- Improved stakeholder trust and reputation: ESG reporting demonstrates a company’s commitment to transparency and accountability, which can improve stakeholder trust and reputation.
- Enhanced risk management: ESG reporting can help companies identify and manage potential risks related to environmental and social issues, such as climate change, human rights violations, and supply chain disruptions.
- Access to capital: ESG reporting can make a company more attractive to investors who prioritize sustainability and social responsibility.
- Increased operational efficiency: ESG reporting can lead to improvements in operational efficiency, such as reducing waste and energy usage, and increasing employee engagement and productivity.
- Regulatory compliance: ESG reporting can help companies comply with existing and emerging regulations related to sustainability and social responsibility.
- Improved long-term financial performance: Companies that prioritize ESG factors and disclose their performance are more likely to generate long-term financial value and outperform their peers.
How are ESG Scores Calculated and Who Assigns Them?
To calculate an ESG score, rating agencies and organizations will typically use a combination of quantitative and qualitative analysis. This can include data from company reports, public disclosures, stakeholder engagement, and third-party sources.
Different agencies and organizations may weigh the importance of each factor differently and use different scoring systems. Some may also provide an overall ESG score, while others may provide separate scores for each factor.
It’s important to note that ESG scores are not standardized and can vary depending on the organization providing the analysis. Therefore, it’s important to understand the methodology and data sources used to calculate an ESG score before making any investment or business decisions based on the score.
ESG scores are measured and reported by a variety of organizations, including rating agencies, data providers, and research firms. Some of the most well-known ESG rating agencies and organizations include:
- MSCI: a global provider of investment decision support tools and services that includes ESG ratings and analysis for companies.
- Sustainalytics: an ESG research and ratings agency that provides data and insights to help investors and companies make informed decisions.
- Moody’s ESG Solutions: a provider of ESG ratings and research that offers a range of tools and services to help investors and companies assess and manage their ESG risks and opportunities.
- FTSE Russell: a global index provider that offers ESG ratings and data to investors and companies around the world.
- CDP: a non-profit organization that provides a global disclosure system for companies to report their environmental impacts and risks.
- ISS ESG: a provider of ESG data, analytics, and ratings that helps investors and companies integrate ESG considerations into their decision-making processes.
There are also many other organizations that offer ESG ratings and analysis, including Bloomberg, Refinitiv, and S&P Global, among others.
What is a Good ESG Score?
A good ESG score can vary depending on the rating agency or organization providing the analysis and the specific industry or sector being evaluated. However, in general, a higher ESG score is considered to be better and indicates that a company is performing well in terms of sustainability and responsible practices.
ESG scores are typically presented on a scale, with higher scores indicating better performance. For example, MSCI’s ESG ratings range from AAA (highest) to CCC (lowest), while Sustainalytics’ ESG ratings range from 0 to 100.
In general, a company with an ESG score in the top quartile (i.e., the top 25%) is considered to be a leader in sustainability and responsible practices. However, it’s important to note that ESG scores are not the only factor to consider when evaluating a company’s sustainability and responsible practices, and different investors may have different thresholds for what they consider to be a “good” score.
Can it be Faked?
Yes, ESG scores can be faked or misrepresented. Some companies may try to present a misleading picture of their sustainability or responsible practices in order to improve their ESG scores and appeal to investors and other stakeholders.
There are several ways that companies may try to fake or misrepresent their ESG practices, including:
- Greenwashing: This is when a company makes false or misleading claims about its environmental or social practices in order to present a more positive image to stakeholders. For example, a company may claim to be “100% renewable” but fail to disclose that this only applies to a small portion of its operations.
- Incomplete disclosure: Companies may fail to disclose important information about their ESG practices or only disclose positive information while ignoring negative impacts.
- Lack of accountability: Companies may make commitments to improve their ESG practices but fail to follow through or provide evidence of progress.
- Poor governance: If a company has poor governance practices, this can undermine the credibility of its ESG practices and ratings.
To avoid falling victim to companies that fake their ESG scores, it’s important to do thorough research and due diligence on a company’s ESG practices and claims. This can include reviewing ESG reports and data, analyzing the company’s performance, and engaging with the company directly to ask questions and request additional information. It’s also important to consider a range of factors beyond just the ESG score, including the company’s overall financial performance and long-term sustainability strategy.