Fleece: Known for its softness, warmth, and durability, this fabric has become a popular choice for comfortable clothing and outdoor gear. However, have you ever wondered about the origins of fleece and its environmental impact? In this article, we’ll explore the answer to the question “What is fleece?” and its effects on our environment.

Understanding Fleece: A Deeper Dive
At its core, fleece is a synthetic material. Traditionally, it’s made from polyester, a petrochemical-based fabric. Its unique structure allows it to trap heat, making it a favorite choice for jackets, blankets, and other insulating garments. However, the comforting embrace of fleece masks its harsher reality.
Fleece is essentially a product of the petrochemical industry, born from crude oil. The transformation process from oil to cozy fleece jacket involves refining oil into a plastic called polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is then extruded into thin fibers. These fibers are weaved together to form the dense, heat-insulating fabric we recognize as fleece.
The Environmental Footprint of Fleece Production
Manufacturing traditional fleece is alarmingly resource-intensive. The extraction and refining of crude oil into PET requires a significant amount of energy, generating substantial carbon emissions in the process. These emissions contribute to the greenhouse effect, leading to climate change. Furthermore, as petroleum resources are finite and non-renewable, their extraction and use in fabric production raise serious sustainability concerns.
Fleece: The Microplastics Menace
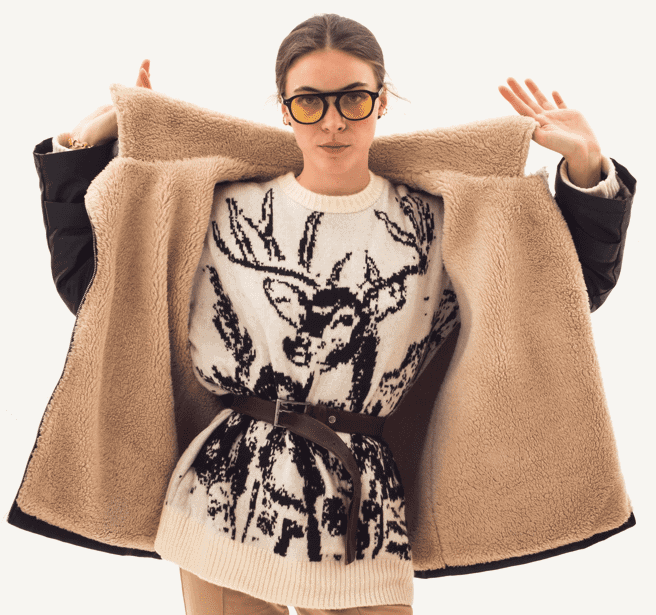

In addition to the carbon footprint and resource depletion associated with fleece production, there’s another less visible but equally serious issue: microplastics. Microplastics are tiny plastic particles, smaller than 5mm in diameter. When a fleece garment is washed, it can shed up to 2,000 of these microfibers per wash. These tiny fibers pass through water treatment plants, entering rivers and oceans where they pose a significant threat to aquatic life. Over time, they enter the food chain, potentially impacting human health.
Pathways to Sustainable Alternities
Despite the environmental issues surrounding traditional fleece, it’s important to note that more sustainable alternatives are available. Fleece can also be made from recycled PET, most commonly derived from used plastic bottles. This recycling process reduces both the amount of plastic waste and the demand for virgin petroleum. Other alternatives include organic cotton fleece and hemp fleece, both plant-based materials that are biodegradable and renewable.
Brands Championing Sustainable Fleece
In an effort to align with the principles of sustainability and conscious consumerism, a number of brands have committed to the use of sustainable fleece in their products. Here, we introduce some of the industry pioneers:
prAna
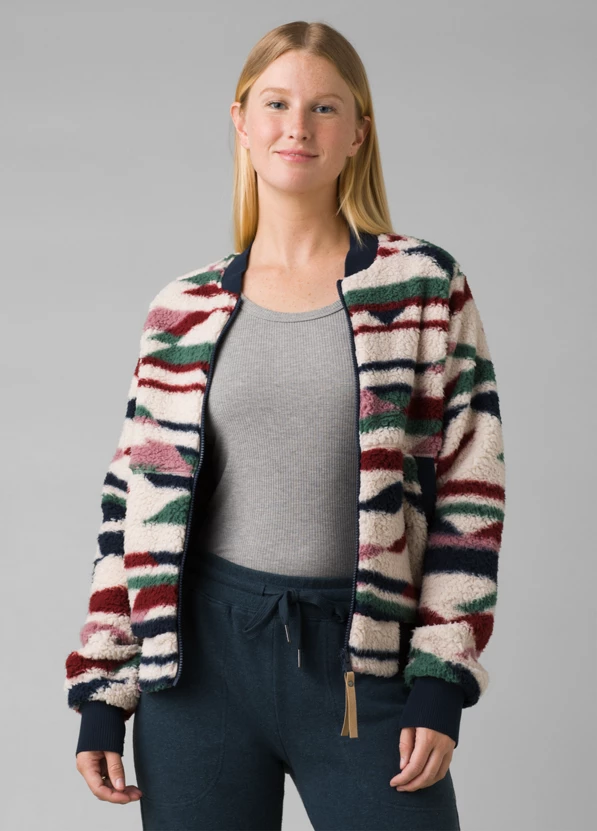

prAna offers a variety of clothing made from sustainable materials, including organic cotton and recycled wool. Their commitment to sustainability and fair trade practices makes them a great choice for conscious consumers.
Outerknown

This brand is committed to creating products that respect the world around us. They offer a range of clothing made from sustainable materials including recycled polyester fleece.
United By Blue
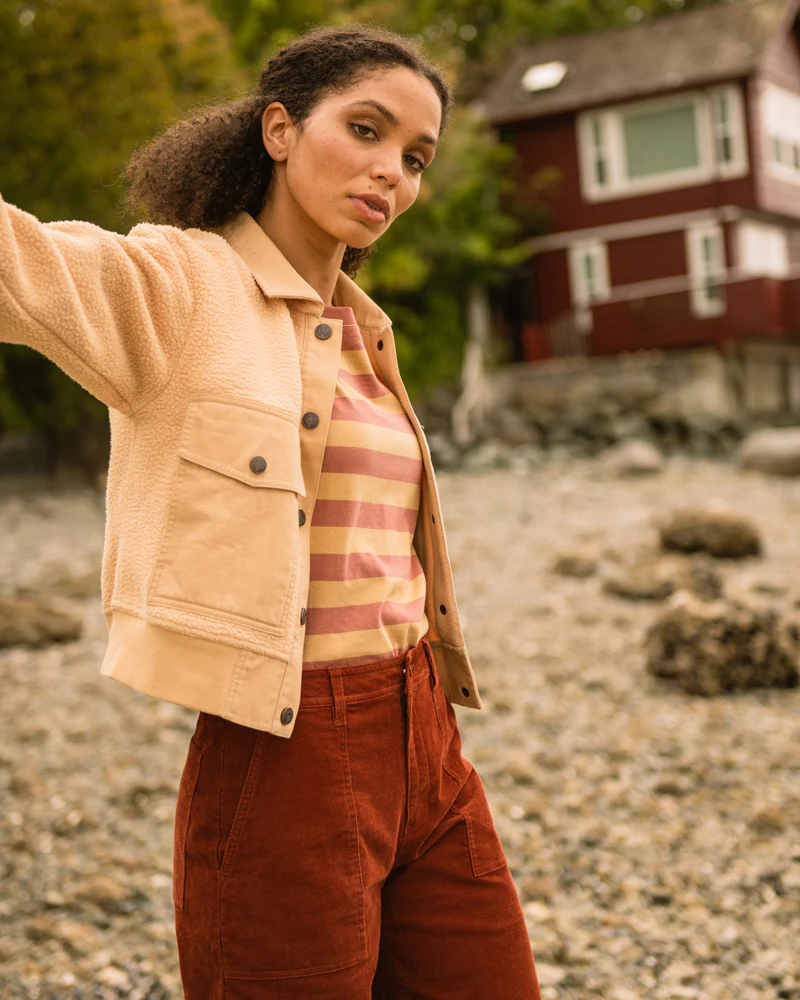

For each product sold, United By Blue removes one pound of trash from the world’s oceans and waterways. They offer a range of outdoor clothing made from sustainable materials, including recycled polyester fleece.
Everlane

Known for its radical transparency, Everlane offers a range of sustainable clothing options. Their ReNew collection includes products made from recycled polyester, reducing their reliance on virgin plastics.
Responsible Fleece Care
As consumers, we can take action to lessen the environmental impact of our fleece products. Washing fleece less frequently reduces energy use and microplastic pollution. Using a fiber-catching bag when washing synthetic garments can help to trap microfibers, preventing them from entering our waterways. Furthermore, by repairing damaged fleece items instead of discarding them, we can extend their lifespan and reduce demand for new products.
The Power of Conscious Consumerism
In conclusion, while fleece as a material has its environmental drawbacks, alternatives are available that align with the principles of sustainability and conscious consumerism. By choosing eco-friendly options and caring for our garments responsibly, we can all contribute to a more sustainable future for fashion.
Understanding the impacts of our choices is the first step towards more conscious consumerism. So next time you shop for a fleece jacket or blanket, remember: your choice has the power to effect change. The journey to sustainability starts with each one of us.
For more insights on fabrics, sustainable alternatives, and responsible brands, be sure to explore our Fashion section. Discover the latest trends and discover conscious fashion choices that align with your values.