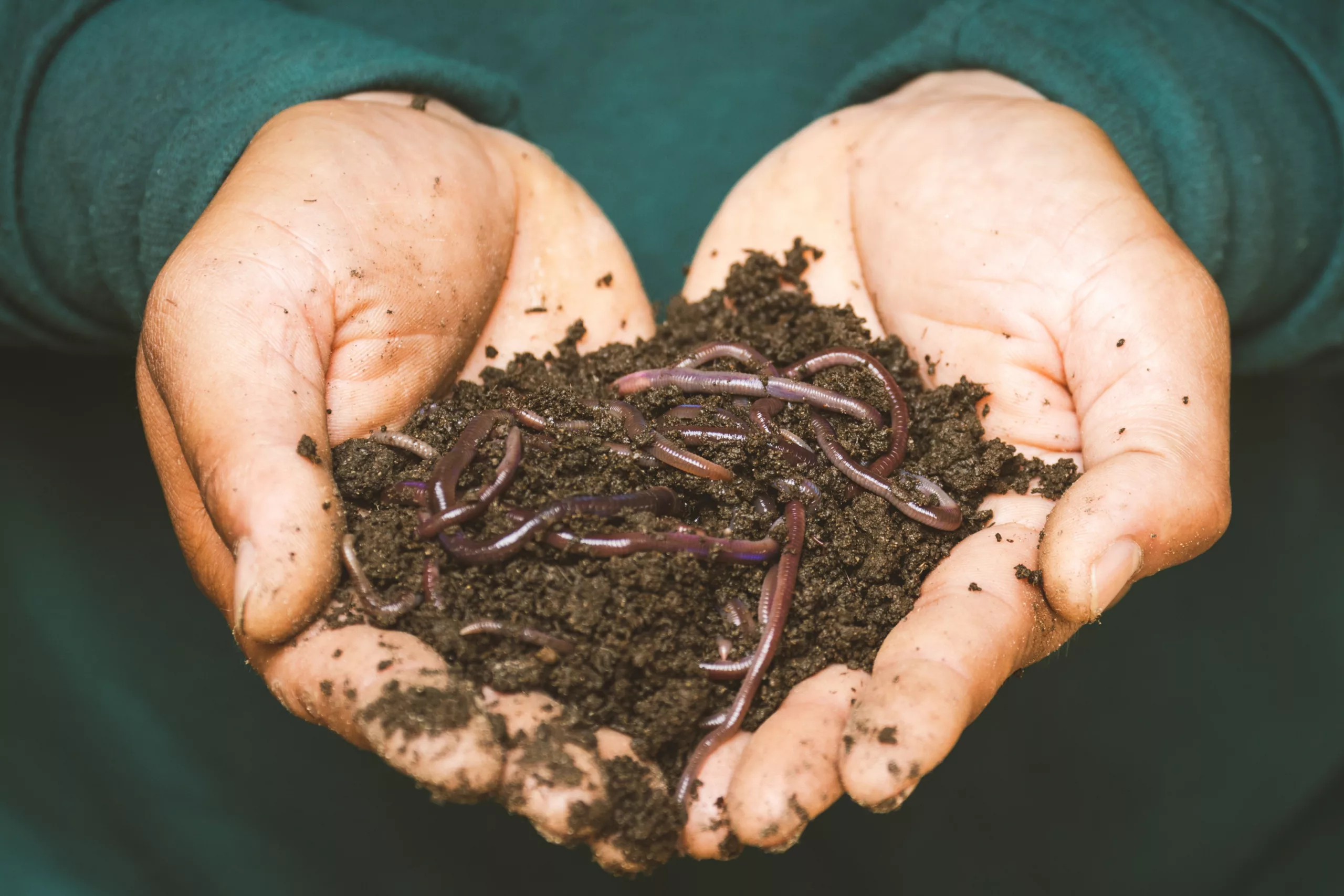
Every living creature on Earth has a specific diet that supports its growth, survival, and reproduction. Worms, though often overlooked, have a crucial role in the ecosystem, and their dietary habits significantly contribute to this role. So, what do worms eat? Worms are decomposers, and their diet primarily consists of organic matter like fallen leaves, decaying plants, and even decomposed animals.
If you’ve ever wondered how the fallen leaves in your yard magically disappear over time, you can thank worms. By consuming these leaves, along with other dead plant material, worms help to recycle organic matter and nutrients back into the soil. But the diet of a worm isn’t just a simple matter of consuming decaying leaves. Different types of worms have different dietary preferences, and these preferences can have significant effects on the soil and the surrounding ecosystem. Let’s dig a little deeper into the world of worms and their fascinating diets.

Types of Worms and Their Diets
Earth is home to an estimated 6,000 species of worms. Among these, some of the most common types include earthworms, composting worms, and marine worms. Each of these worms has a unique diet related to their specific habitat.
Earthworms
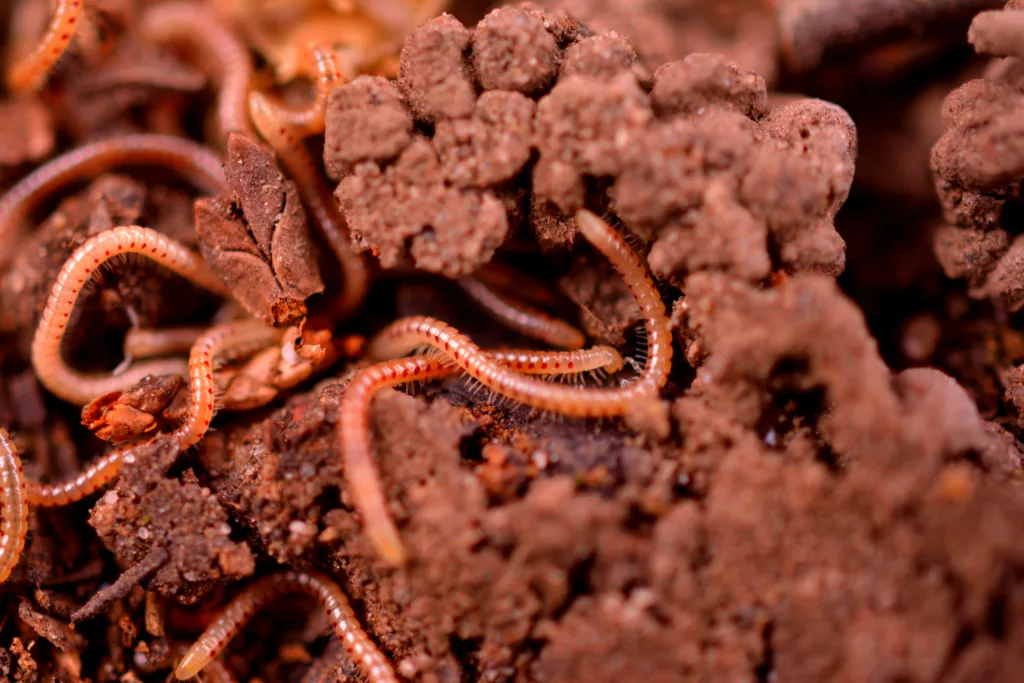

Earthworms, also known as ’nature’s plow,’ are soil-dwelling worms that consume soil and the organic matter within it. They eat this material, digest it, and then excrete it in the form of castings, rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for plant growth, making earthworms critical contributors to soil fertility.
Composting Worms
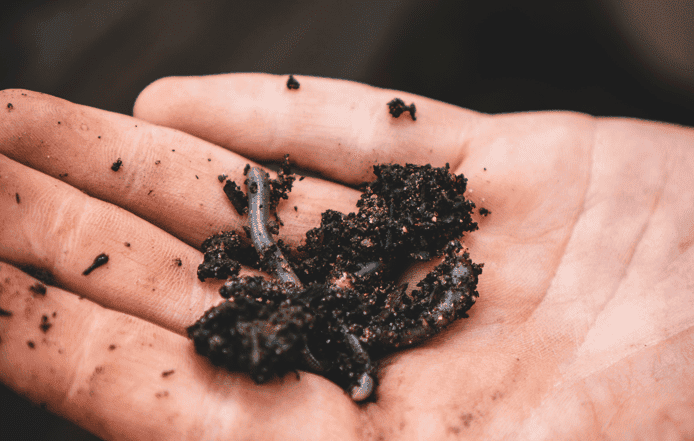

Composting worms, also known as red worms or red wigglers, have a slightly different diet. These worms thrive on organic waste such as fruit and vegetable peelings, coffee grounds, and eggshells. Unlike earthworms, composting worms live near the surface of the soil and prefer a diet rich in organic material, making them the perfect composting partners.
Marine Worms

Marine worms, as their name suggests, inhabit the world’s oceans. They have a diverse diet that can include algae, plankton, and other microscopic organisms. Some species are even scavengers, consuming dead organisms that sink to the ocean floor.
Deep Dive: What do Composting Worms Eat
Composting worms, or red worms, are the unsung heroes of a garden compost pile. They have a voracious appetite for organic waste, and they can eat and process their body weight in food each day. But what exactly do they eat?
Composting worms love fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, tea bags, grains, and eggshells. However, they do have some dietary restrictions. Foods that are highly acidic, like citrus fruits and tomatoes, can harm worms. They also avoid dairy products, meats, and oily foods, as these can create unpleasant odors and attract pests to your compost pile.
Not only do composting worms help reduce kitchen waste, but they also produce a valuable byproduct known as worm castings. These castings are a form of organic fertilizer that’s rich in nutrients and beneficial for plant growth.
The Role of Worms in Decomposition and Soil Fertility

Decomposition is a natural process that breaks down organic matter into simpler substances. This process is crucial for recycling nutrients in the ecosystem, and worms play a significant role in it.
As worms consume organic matter, they break it down into smaller particles. These particles are then further decomposed by bacteria and other microorganisms in the soil. The end result is a nutrient-rich substance that can be easily absorbed by plant roots.
In addition to aiding decomposition, worms also improve soil structure. As they burrow through the soil, they create channels that allow air and water to penetrate more deeply. This aeration of the soil makes it more hospitable for plant roots and beneficial soil microorganisms.
Worm Castings: A Nutrient-Rich Byproduct
One of the most beneficial byproducts of a worm’s diet is worm castings. This dark, crumbly substance is essentially worm poop, but it’s also a goldmine for plants.
Worm castings are rich in nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for plant growth and are readily available in worm castings, making them a potent organic fertilizer. In addition, worm castings improve soil structure and increase its water-holding capacity, further benefiting plants.
But the benefits of worm castings don’t stop there. They also contain beneficial microorganisms that can help suppress plant diseases and pests. By introducing these microorganisms into the soil, worm castings can contribute to a healthier, more robust garden.
Vermiculture: Worms in Home Composting
Vermiculture, or the cultivation of worms, is a practical way to reduce kitchen waste, produce nutrient-rich compost, and contribute to a healthier garden. By maintaining a worm composting bin at home, you can provide a suitable habitat for composting worms and reap the benefits of their work.
Starting a worm composting bin is relatively straightforward. All you need is a suitable container, bedding material like shredded newspaper or cardboard, a handful of soil, and of course, composting worms. Once your bin is set up, you can start adding your kitchen scraps and watch as the worms transform them into valuable compost.
Maintaining a worm composting bin is also quite simple. Regularly add fresh food scraps, keep the bin in a location with a stable temperature, and make sure the bedding stays moist but not wet. With these simple steps, you can keep your composting worms happy and productive.
How to Make and Use Compost Tea with Worm Castings
One of the lesser-known benefits of worm castings is the ability to create compost tea. This nutrient-rich liquid can provide a quick boost to your plants and is simple to make.
To make compost tea, you’ll need worm castings, water, and a bit of time. Simply place the worm castings in a bucket, add water, and let the mixture steep for 24 to 48 hours. After steeping, strain the liquid, and your compost tea is ready to use.
Compost tea can be applied directly to the soil around your plants, or it can be used as a foliar spray. When used as a soil drench, compost tea provides plants with a quick nutrient boost, promoting healthier growth. As a foliar spray, it can help protect plants from diseases and pests.
Worms and Sustainable Living

Worms may be small, but their impact on the environment is significant. By consuming organic waste and converting it into nutrient-rich compost, worms help reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. This process, known as vermicomposting, is a practical and eco-friendly way to manage organic waste.
In addition, using worm castings or compost tea as an organic fertilizer can contribute to a more sustainable gardening practice. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, these organic alternatives do not contribute to water pollution, and they help to maintain healthy soil life.
Conclusion: Worms’ Diet
In conclusion, worms’ diet plays a significant role in maintaining soil fertility, promoting plant growth, and managing organic waste. While their diet largely consists of decomposed organic material, the specifics can vary depending on the type of worm. By understanding what worms eat and how they contribute to the ecosystem, we can appreciate their role in nature and utilize their abilities in our composting practices.
Their voracious consumption of organic waste not only helps reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, but it also produces valuable byproducts like worm castings and compost tea. These organic fertilizers can greatly enhance the health and productivity of our gardens. For those interested in more sustainable living practices, starting a worm composting bin at home can be a great step. It’s a practical way to recycle kitchen waste, and it provides a continuous supply of high-quality compost for your plants.
Ready to start your composting journey and enrich your garden with nutrient-rich compost tea? Check out our compost tea recipe blog now and take the first step towards a greener and more sustainable lifestyle. Get started and watch your garden thrive!