As World Water Week 2023 approaches, the global community turns its attention to the pressing issue of water preservation. In today’s rapidly changing environment, the importance of conserving our precious water resources cannot be overstated.

Background
World Water Week has been an annual focal point for the globe’s water issues since its inception. It serves as a platform for collaboration and the exchange of ideas to address the current water preservation challenges. With the looming global water crisis, the need for sustainable water management is more critical than ever.
World Water Week 2023: Seeds of Change

Credits: newsrooompost
World Water Week 2023, taking place from August 20 to 24 in Stockholm, Sweden, is themed “Seeds of Change: Innovative Solutions for a Water-Wise World.” This event encourages a re-envisioning of how the world manages water and explores solutions to water-related challenges. The conference will be held both online and in-person at the Waterfront Congress Center in Stockholm.
It is the leading conference on global water issues, curated by Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) and convened by world-leading organizations. The conference covers a wide range of topics, including the water impacts of climate change, biodiversity loss, poverty, food security, agriculture, health, technology, and more.
Highlighted Events:
- Aligning and Accelerating Collective Action for Water Stewardship: This session focuses on collective action challenges and presents a new publication on the subject. It aims to align thinking, geographies, and understanding of ground-level capacity, as well as reassess how shared work is funded.
- Developing a Payment for Ecosystem Services Framework in Ethiopia: This session delves into the challenges faced by the Koga irrigation reservoir in Ethiopia and the potential of a Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES) scheme to address them.
- Water in Business: From Commitments to Transformation: This discussion will focus on how to ensure that commitments made during the UN Water Conference in March translate into substantive change and action.
- Innovation and the Geopolitics of Water: This session explores the role of digital change in transboundary water cooperation and water diplomacy as preventive peace mediation.
Eco-Friendly Alternatives for Water Preservation
Water is the lifeblood of our planet, and its preservation is paramount for the survival of all living organisms. As the global population burgeons and urbanization expands, the demand for freshwater has skyrocketed, making the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives for water preservation more crucial than ever. Let’s delve deeper into these sustainable practices:
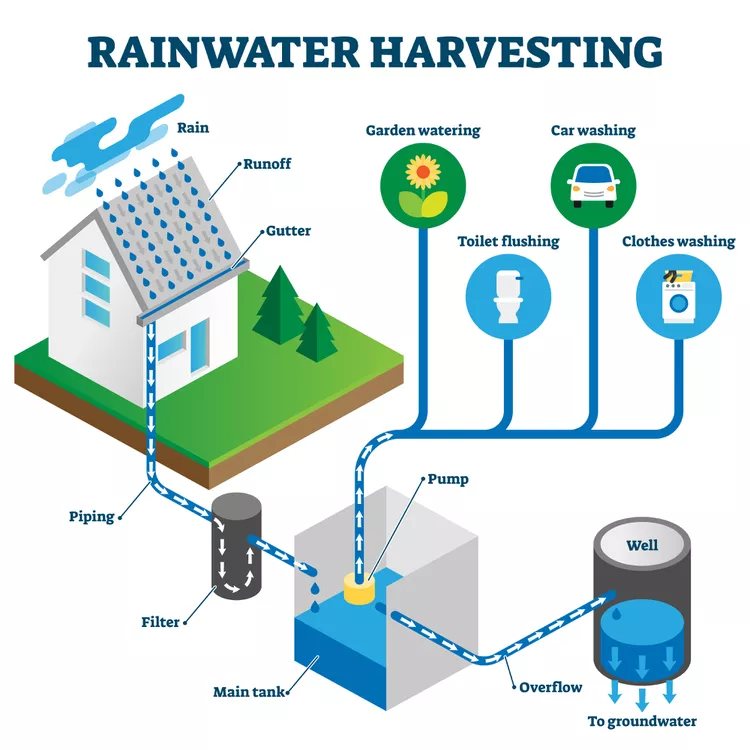
1. Rainwater Harvesting:
- Historical Relevance: Ancient civilizations, from the Romans to the Indus Valley inhabitants, have utilized rainwater harvesting techniques, recognizing the value of capturing and storing rainwater for future use.
- Modern Applications: In contemporary settings, rainwater harvesting systems are equipped with advanced filtration units, making the collected water suitable for various purposes, from gardening to toilet flushing, and even drinking when purified adequately.
- Environmental Impact: Beyond water conservation, these systems reduce runoff, which can lead to erosion and the transportation of pollutants to local waterways.
Credits: Treehugger
2. Greywater Recycling:
- Resource Efficiency: Greywater constitutes about 50-80% of a household’s wastewater. Recycling this water is a testament to the adage, “Waste not, want not.”
- Applications: While greywater may not be potable, it’s perfectly suited for landscape irrigation, toilet flushing, and even laundry, given appropriate treatment.
- Ecological Benefits: By diverting greywater from sewage, we reduce the energy and chemicals required for wastewater treatment, thereby minimizing environmental impact.

Credits: NPCC
3. Sustainable Agriculture Practices:
- Drought-Resistant Crops: Plants like millets, sorghum, and certain legumes have evolved to thrive in arid conditions. Cultivating these crops can lead to significant water savings.
- Efficient Irrigation: Techniques like drip irrigation and soaker hoses target the root zones, minimizing water wastage through evaporation or runoff.
- Soil Health: Healthy soils, rich in organic matter, retain moisture better. Practices like mulching and composting enhance soil health, leading to reduced irrigation needs.

4. Wetland Restoration and Conservation:
- Nature’s Purifiers: Wetlands are often dubbed the “kidneys of the Earth.” They trap pollutants, including harmful bacteria, heavy metals, and pesticides, ensuring cleaner water downstream.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Wetlands are habitats for a myriad of species, from migratory birds to aquatic plants. Their conservation ensures the survival of these species.
- Flood Control: Acting as natural sponges, wetlands absorb excess rainfall and reduce flooding risks in adjacent areas.
- Carbon Sequestration: Wetlands play a crucial role in capturing and storing carbon dioxide, making them invaluable in the fight against climate change.

Benefits of Eco-Friendly Alternatives: A Deeper Dive
Eco-friendly alternatives, often termed “green solutions,” have been gaining traction globally due to their multifaceted benefits. These benefits span across environmental, economic, and social dimensions, creating a holistic impact on our planet and its inhabitants. Let’s delve deeper into these benefits:

1. Environmental Benefits:
- Biodiversity Conservation: Eco-friendly practices often lead to the preservation of natural habitats, ensuring diverse species continue to thrive.
- Reduction in Pollution: Green solutions, especially in industries, reduce the emission of harmful pollutants, ensuring cleaner air and water.
- Conservation of Resources: Sustainable practices ensure that natural resources, such as water and minerals, are used judiciously, ensuring they last for future generations.
- Mitigation of Climate Change: By reducing carbon footprints, eco-friendly alternatives play a pivotal role in slowing down global warming and its detrimental effects.

2. Economic Benefits:
- Cost Savings: In the long run, sustainable solutions often prove to be cost-effective. For instance, solar panels might have an upfront cost, but they lead to significant savings on electricity bills over time.
- Job Creation: The green industry, from renewable energy to organic farming, has been a source of job creation, offering opportunities in new and emerging sectors.
- Reduction in External Costs: Eco-friendly practices reduce the external costs associated with pollution, such as healthcare costs for diseases caused by environmental pollutants.
- Boost to Local Economies: Sustainable practices, like local farming or eco-tourism, can invigorate local economies, ensuring money remains within the community.

3. Social Benefits:
- Health and Well-being: A cleaner environment leads to fewer health issues. Reduced pollutants mean fewer respiratory diseases, allergies, and other health problems.
- Cultural Preservation: Many eco-friendly practices, especially in tourism and agriculture, help in preserving indigenous cultures and traditions.
- Community Engagement: Green initiatives often foster community involvement. Whether it’s a community garden or a local clean-up drive, such initiatives bring people together for a common cause.
- Education and Awareness: The move towards sustainability has led to increased awareness and education about the environment. Schools and institutions are now incorporating eco-consciousness into their curriculums, creating a more informed generation.
Case Studies
Several real-world examples highlight the impact of eco-friendly water preservation projects:
- Gresham’s Wastewater Treatment Plant: Through biogas generation and recovery, this plant in the Pacific Northwest generates more electricity than it consumes annually, saving the city about $500,000 per year.
- DC Water’s Blue Plains Advanced Treatment Plant: By adopting the thermal hydrolysis process, the plant generates 10 megawatts of electricity, covering about one-third of its energy requirement.
- East Bay Municipal Utility District (EBMUD) in Oakland, CA: By accepting organic wastes, EBMUD’s wastewater treatment plant doubled its biogas production, becoming North America’s first facility to produce more renewable energy than required.
- Singapore’s NEWater: Singapore’s NEWater is a prime example of how advanced water treatment technologies can be used to recycle wastewater. The treated water is so pure that it is often mixed with reservoir water and then undergoes conventional treatment to be used as potable water. This initiative has significantly reduced Singapore’s dependence on imported water.

- Orange County Groundwater Replenishment System: Located in California, this system takes treated wastewater and purifies it using advanced techniques like reverse osmosis. The purified water is then injected into the groundwater basin. This project not only provides a sustainable water source but also prevents seawater intrusion.
- Windhoek’s Direct Potable Reuse Plant: In Namibia, the city of Windhoek has been recycling wastewater for direct potable use since the 1960s. The plant uses a multi-barrier approach, including ozonation and activated carbon filtration, to ensure the water’s safety and quality.
- El Paso’s Advanced Water Purification Facility: El Paso, Texas, has developed an advanced water purification system that transforms treated wastewater into drinking water. The process involves multiple purification steps, ensuring the water meets all federal and state drinking water standards.
- Melbourne’s Eastern Treatment Plant: In Australia, the Eastern Treatment Plant in Melbourne uses advanced tertiary treatment to purify wastewater. The treated water is then used for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation and industrial use, reducing the demand for freshwater sources.
Future of Water Preservation

AI and IoT in Water Management
Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping water preservation. AI offers predictive analysis, leak detection, and real-time water quality monitoring. Meanwhile, IoT devices, such as smart meters and automated irrigation systems, optimize water consumption and enhance wastewater treatment.
Filtration and Sustainable Infrastructure
Innovative filtration methods, from nano filters to biofiltration, are ensuring cleaner water sources. Concurrently, sustainable infrastructures like green roofs and permeable pavements are capturing rainwater, reducing urban runoff, and aiding groundwater recharge.
Community Initiatives
Grassroots movements are promoting rainwater harvesting and fostering a water-conscious mindset. These community-driven efforts, combined with technology and sustainable infrastructure, are pivotal for the future of water preservation.
Conclusion
The eco-friendly alternatives for water preservation are not just options but necessities. As we commemorate World Water Week 2023, let’s pledge to make every drop count and ensure a water-secure future for all.
Eager to keep up with the latest in sustainability? Dive into our blogs and immerse yourself in the newest trends, innovations, and insights in the world of eco-friendly living.